客服电话:021-61998208
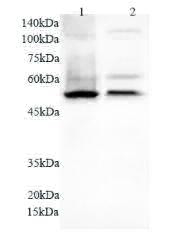

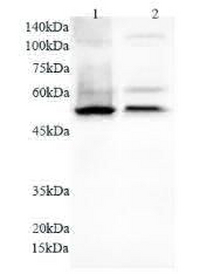
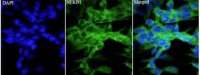
Anti NFkB1 polyclonal antibody
Anti NFkB1 polyclonal antibody
应用:WB,ICC,IHC
产品名:Anti NFkB1 polyclonal antibody
货号:KLP155
种类(Category)
Primary antibody
宿主(Host)
Rabbit
反应种属(Species specificity)
Human,other species was not test
应用实验(Tested applications)
WB:1:2000~1:8000,ICC:1:50~200,IHC:1:50~100
克隆性(Clonality)
Polyclonal
偶连物(Conjugation)
Unconjugated
免疫原(Immunogen)
Recombinant protein of human NFkB1(Met248-Ile366).
别名
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit,DNA-binding factor KBF1,EBP-1,Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1,NFKB1,DNA binding factor KBF1,EBP 1,KBF1,NF kappa B,NFKB p105,NFKB p50,NFKB1,NFKB1,p105,NFKB1,p105,p50,nfkb1a,p105,p50
状态(Form)
Liquid
储存溶液(Buffer)
PBS,pH7.4,containing 0.05% proclin300,50% glycerol.
存放条件(Storage)
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles.Store at 4°C for frequent use.Store at -20 to -80 °C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
浓度(Concentration)
0.75mg/ml
亚型(Isotype)
IgG
分子量(MW)
105kDa
纯化方式(Purity)
Antigen affinity purification
产品背景:NFkB is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NFkB is activated by various intra- and extracellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. NFkB is a family of transcription factors that consists of homo- and heterodimers of NFkB1/p50 and RelA/p65 subunits, and controls a variety of cellular events including development and immune responses. All members share a conserved amino terminus domain that includes dimerization, nuclear localization, and DNA binding regions, and a carboxy terminal transactivation domain. Serines 529 and 536 in the transactivation domain of RelA/p65 are phosphorylated in response to several stimuli including phorbol ester, IL1 alpha and TNF alpha as mediated by IkB kinase and p38 MAPK. Phosphorylation of serines 529 and 536 is critical for RelA/p65 transcriptional activity. Activated NFkB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFkB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFkB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. This antibody can bind p105 isoforms of NFKB1.