客服电话:021-61998208

核因子κB2(NFkB2)重组蛋白
核因子κB2(NFkB2)重组蛋白
Recombinant Nuclear Factor Kappa B2 (NFkB2)
LYT-10; H2TF1; Lymphocyte translocation chromosome 10; Nuclear Factor Of Kappa Light Polypeptide Gene Enhancer In B-Cells 2(p49/P100); Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p52
[ PROPERTIES ]
Residues: Pro38~Leu343
Tags: Two N-terminal Tags, His-tag and T7-tag
Accession: Q00653
Host: E. coli
Subcellular Location: Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
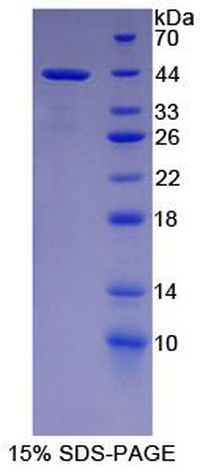
Purity: >95%
Endotoxin Level: <1.0EU per 1μg
(determined by the LAL method).
Formulation: Supplied as lyophilized form in 20mM Tris,
500mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT,
0.01% sarcosyl, 5% trehalose, and preservative.
Predicted isoelectric point: 9.5
Predicted Molecular Mass: 38.5kDa
Accurate Molecular Mass: 42kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE reducing conditions.
Applications: SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP.
(May be suitable for use in other assays to be determined by the end user.)
Note: The possible reasons that the actual band size differs from the predicted are as follows:
1. Splice variants: Alternative splicing may create different sized proteins from the same gene.
2. Relative charge: The composition of amino acids may affects the charge of the protein.
3. Post-translational modification: Phosphorylation, glycosylation, methylation etc.
4. Post-translation cleavage: Many proteins are synthesized as pro-proteins, and then cleaved to
give the active form.
5. Polymerization of the target protein: Dimerization, multimerization etc.
[ USAGE ]
Reconstitute in ddH2O.
[ STORAGE AND STABILITY ]
Storage: Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Store at 2-8oC for one month.
Aliquot and store at -80oC for 12 months.
Stability Test: The thermal stability is described by the loss rate of the targetprotein. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test,that is, incubate the protein at 37oC for 48h, and no obvious degradation andprecipitation were observed. (Referring from China Biological Products Standard,which was calculated by the Arrhenius equation.) The loss of this protein is lessthan 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
[ SEQUENCES ]
The sequence of the target protein is listed below.
PYL VIVEQPKQRG FRFRYGCEGP SHGGLPGASS EKGRKTYPTV KICNYEGPAKIEVDLVTHSD PPRAHAHSLV GKQCSELGIC AVSVGPKDMT AQFNNLGVLH VTKKNMMGTMIQKLQRQRLR SRPQGLTEAE QRELEQEAKE LKKVMDLSIV RLRFSAFLRA SDGSFSLPLKPVISQPIHDS KSPGASNLKI SRMDKTAGSV RGGDEVYLLC DKVQKDDIEV RFYEDDENGWQAFGDFSPTD VHKQYAIVFR TPPYHKMKIE RPVTVFLQLK RKRGGDVSDS KQFTYYPLVEDKEEVQRKRR KAL
[ REFERENCES ]
1. Schmid R.M., et al. (1991) Nature 352:733-736.
2. Bours V., et al. (1992) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:685-695.
3. Thakur S., et al. (1994) Oncogene 9:2335-2344.
4. Liptay S., et al. (1994) Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:7695-7703.
特别提示:本公司的所有产品仅可用于科研实验,严禁用于临床医疗及其他非科研用途!